How do the characteristics of historic urban landscapes influence public sentiments, and what implications do these findings have for urban planning and development strategies?
In 2011, UNESCO issued The UNESCO Recommendation on the Historic Urban Landscape (“The Recommendation” hereafter), introducing the concept of “historic urban landscape” (HUL). HUL is defined as “the urban context and its geographical setting taking into consideration the historical layering of cultural and natural values and attributes”. It is noteworthy that ancient towns or historic cities, as an important subclass of HUL, have garnered increasing attention. In recent years, public perception and emotional experience of physical environments have become a focal point in urban studies, which, however, is less combined with HUL in academic efforts. Existing scholarly research predominantly focuses on public perception on the image of HUL, with subjects such as visual image perception of HUL based on digital footprints, evaluation of HUL based on online reviews, and heritage identity perception. In these studies, public sentiments and feelings are merely considered as indicators or representations of HUL perception, and their relationship with HUL preservation and sustainable development has not been fully explored.
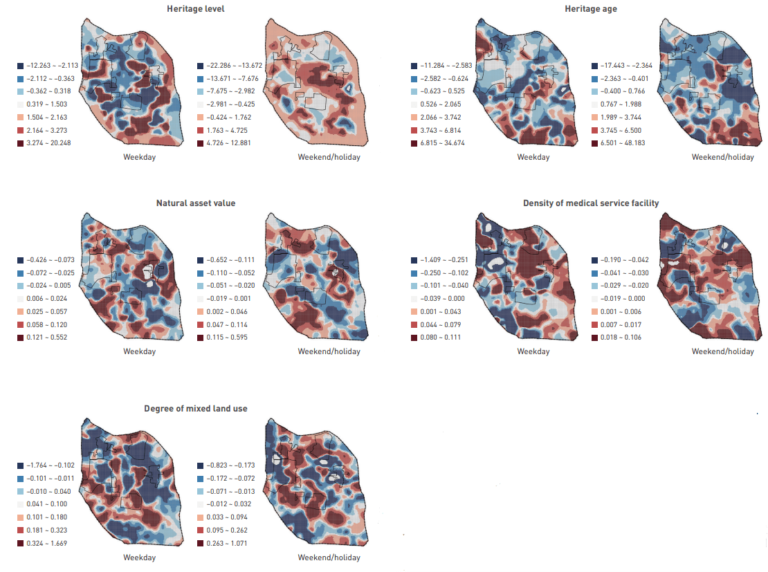
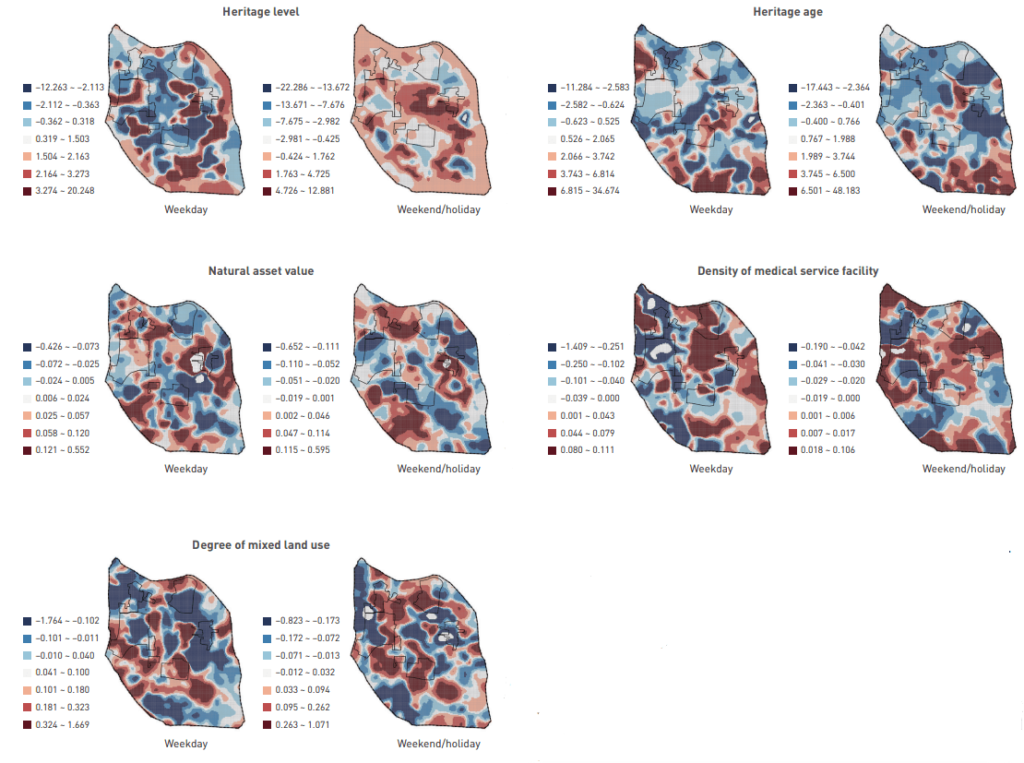
To elucidate the dynamic evolution process from identifying HUL characteristics to the public’s emotional responses, this study constructs an HUL–Cognition–Sentiment (HCS) analysis framework—consisting of three dimensions of heritage intrinsic value, urban functional value, and urban landscape value—and explored the spatio-temporal patterns of public sentiments and the influencing mechanisms of HUL characteristics on public sentiments in the Shaoxing ancient city.
The study employed ArcGIS Pro analytical tools to perform the model credibility analysis on the scores of public sentiments on weekdays and weekends/holidays with the aforementioned 11 explanatory variables, and has been published on the journal of Landscape Architecture Frontiers and entitled “Research on the Influencing Mechanism of Historic Urban Landscape Characteristics on Public Sentiments and the Spatio-temporal Differentiation Patterns—A Case Study of Shaoxing Ancient City in Zhejiang Province, China”.
The results show that different HUL characteristics had played varied influencing mechanisms on public sentiments, and the effects of same HUL characteristics on public sentiments also vary between weekdays and weekends/holidays and among different HULs. On weekends/holidays, public sentiments were more influenced by the intrinsic value factors of HUL (e.g., heritage level, heritage age), whereas on weekdays, they were more affected by urban functional value factors (e.g., density of transportation facilities), and urban landscape value factors (e.g., degree of mixed land use) played a greater role in arousing people’s positive sentiments.
It is important to note that the influence of HUL characteristics on public sentiments is not static. Urban designers should propose more targeted development planning and policies based on the local impact characteristics of HUL on public sentiments. This aligns with the core idea of HUL, which is to balance HUL preservation with urban development through comprehensive urban planning and management measures, thereby achieving a sustainable urban environment and enhancing people’s well-being.
Bibliographic information:
Press release from Frontiers Journals.